
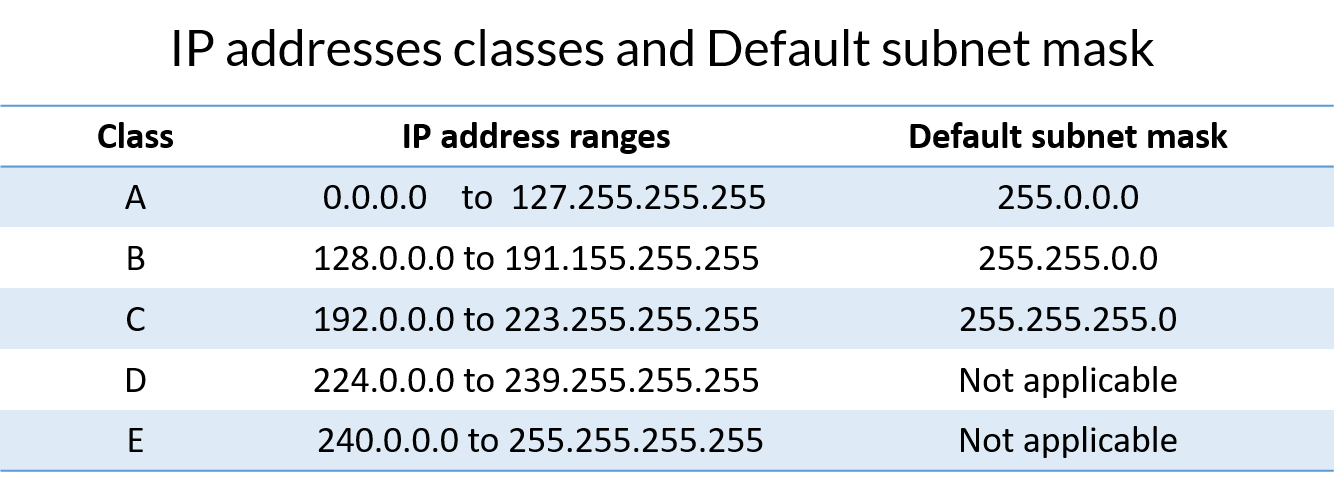
Class B allows for 16,384 networks by using the first two octets for the network ID.

The four octets that make up an IP address are conventionally represented by a.b.c.d - such as 127.10.20.30.Īdditionally, information is also provided on private addresses and loop address (used for network troubleshooting). The list below shows the five available IP classes, along with the number of networks each can support and the maximum number of hosts (devices) that can be on each of those networks. Class D and class E are for special uses. Primarily, class A, B, and C are used by the majority of devices on the Internet. Each class has a specific range of IP addresses (and ultimately dictates the number of devices you can have on your network). In the IPv4 IP address space, there are five classes: A, B, C, D and E.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
